Plastic products are manufactured by injection molding Machines, the most common mass production method. These products include chairs, toys, consumer cases, and electronics. Disposable Cutlery injection. During the 19th century, molding was invented to solve billiards’ problems. A billiard ball was made from ivory harvested from the tusks of African elephants. This resulted in the decimation of the elephant population. Consequently, a billiards manufacturer offered a ten-thousand-dollar prize for the replacement of ivory
One of the first plastics celluloid billiard balls was created by John Wesley Hyatt. He created a device for moulding celluloid items. In theory, this device marked the beginning of plastic injection moulding. Simple moulding involves injecting melted plastic into a mould. Await cooling After that, a plastic product that is not real appears. Injection. Injection moulding machines are used in the sophisticated and complicated process of moulding.
Hi-Tech Plastics Engineering is the only company in Pakistan that provides complete turnkey solutions for any type of plastics item, whether it is in plastic household items or in medical parts.
Hi-Tech Plastics Engineering has its head office in Lahore, as well as branches in Karachi and China, and we are now preparing for our grand opening in Dubai.

These products are made by Plastics molding machine

Major Parts of Injection Molding Machine
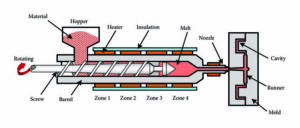
The injection unit, the mould, and the clamp are its three primary constituents. The injection unit’s hopper receives plastic pellets, which are then injected into the barrel by a screw and advanced by heating bands wrapped around the barrel. The plastic pellets should be heated as the screw advances them. They begin to melt towards the barrel’s base and are totally liquid by the time they exit the spout. So, let’s just stop talking about it. Plastic melts in front of the screw and pushes forward like the plunger of a syringe.
Injection Unite of Plastic Molding Machine
The screw injects molten plastic into the empty part of the mold known as the cavity image in a matter of seconds, and the plastic solidifies. The mold opens in less than a minute. When the part is ejected, the mold closes and the process begins again. All injection-molded objects begin with these plastic pellets, which are a few millimeters in diameter. Before the twentieth century, they could be mixed with small amounts of a pigment called colorant or with up to 15% recycled material and then fed into an injection molding machine.
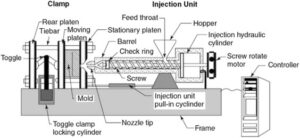
injection Molding machinery only heated the barrel from the outside to melt the plastic before injecting the molten material, but because plastic conducts heat inefficiently, the temperature in the Barrow was uneven. The revolving screw is frequently recognized as the most significant invention that transformed the plastics industry in the 20th century. Either the middle was too chilly and not fully melted, or the outer sections were too hot and disintegrated, leaving the plastic.
Injection Molding Machine Screw and barrel System
Early plunger-style devices had a plastic-filled barrel. As you know, the plastic’s temperature wasn’t consistent. The reciprocating screw does three things. In earlier and newer machines, plastic just touches the screw shaft. This eliminates the cooler core. needing a thin, evenly-heated plastic layer. Screw flights wrap around the shaft as the screw rotates. Raw materials are flown via the arrow.
Flights evenly combined plastic, screw motion, agitators, and melting pellets. Third, as the screw heats up, the chef’s plastic diameter extends along the screw, reducing the gap between the chef and the wall. The flights advance the plastic while compressing the pellets against the barrel wall. Shearing heats plastic throughout.
To everyone’s astonishment, the majority of the heat needed to melt the plastic is between 60 and 90%. Molten plastic from heating bands goes beyond the screw’s front through grooves or flutes. When enough plastic is present to fill the mould. It instantly plunges plastic into the mould. As the screw moves, a check ring is pressed against a thrust ring to prevent backflow.
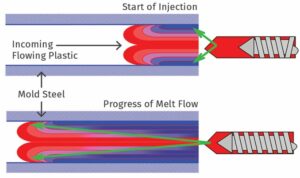
This first constrains The Attic to the predetermined form. Air is expelled from the mold as molten plastic is poured, and the resulting gas fills the cavity. The mould features ventilation channels built into the landing surface. When heated, the plastic has the consistency of honey and is only 5–40 microns thick, making it too thick to easily pass through the narrow openings. Substance used to slow the solidification of the plastic
Typically, water travels in channels just beneath the mold’s surface.
After the injected area has set, the mold’s opening creates a significant suction due to the mold’s interior expanding without adding air. In response, the mould progressively grew larger by a few millimetres at first, releasing the vacuum as air rushed in. The mould quickly releases the last section. In order to disassemble the part. These precision-machined steel moulds can cost thousands of dollars.
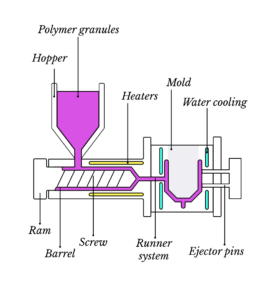
When the plastic couch is involved, removing the part from the mould can be challenging. The built-in ejector pins that push the part of the mould, the ends of the pins, sit flush with the core half of the mould, but are not completely aligned, as it cools it shrinks and so becomes stuck tightly on the core half of the mould. They can occasionally protrude or have little dents. Therefore, if you closely inspect moulded objects, you will notice circular ejector pin witness markings. This chair, for instance, has numerous witness markings on the bottom. An operator must remove the plastic sprue that linked the injection unit to the mould when the item drops into the mould.

Runner of the Mold
Spruces are fastened to items by manually twisting or cutting off screws from the part. Only in moulds that produce a single part at a time, such as a chair or smaller object made in multiples in a single mould, does the sprue connect to the part itself. Instead, it does so via a network of distribution tunnels known as runners that fan out from the sprue and next to each cavity in the mould.
The gate can be seen on plastic. Cutlery and model aeroplane parts. Typically, Runners arrive with their moulds intact. Always have at least two pieces, and the dividing line on this piece of meat is where the mouldy flesh bits are referred to. Cutlery. Along the side of the fork, The Parting line is seen. Mold halves are never joined with crisp corners and perfect alignment.

Parting line on the Plastics Mold
The draught angle, which creates a clear separating line on the moulded object, is an additional critical aspect of mould design. Because it is an interior area, ejection from a room with walls that are exactly 90 degrees will be extremely difficult. The core of the mould will be scraped away by the walls. In addition, it will be difficult to break the vacuum because there is no simple entrance. However, the component can be removed considerably more quickly if the walls are tapered, even by just one or two degrees. This is due to the fact that, as the component moves slightly, the walls are no longer in contact with the core half and can therefore surge in as one.
The Lego brick is an excellent example of injection moulding. Although the injection point is visible in the centre of the diagram, it is neither a gate nor a sprue since Lego moulds employ hot Runners, which are heated distribution networks. Thus, the plastic in the runners and in the mould remains molten. These leaves are solidified without the need to remove gates or fasteners. The manufactured bricks are expelled. ability is usable. The disadvantage of the system is that it is more expensive than a traditional cold runner system.
on the lower edge of the brick. Ejector pin witness marks are visible, but I find the Lego designs the most clever. Their draught angle necessitates that the ego brick’s exterior be square.
QNA for injection molding machine
What are molding and its types?
The five most common and reliable plastic molding processes are as follows. There are five main categories of plastic molding processes: extrusion, compression, blow, injection, and rotating.
What is injection molding used for?
Injection molding involves pouring molten plastic into a mold, cooling, and hardening it. The approach is used for mass-producing complex-shaped plastic goods.
What is the injection Molding machine process?
During the process of injection molding, a thermoplastic polymer is heated to a temperature that is higher than its melting point. This causes the solid polymer to be transformed into a molten fluid that has a viscosity that is just slightly higher than water. This molten material is mechanically pushed, also known as injected, into a mold that is already shaped to the final product that is required.
What is an example of injection molding?
Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing method used to create many different types of components. Examples include appliance housings, electrical circuit boards, bottle caps, toys, jewel boxes, and components of portable potties; medical equipment like needles or surgical gadgets; and components of automobiles like piping systems, windshield switches, and handles.
What are the 3 main parts of the injection mold?
The 3 major components of an injection molding machine are the base, the hopper, the barrel, and the clamping unit. Additionally, there are minor components including the nozzle, ejector pins, split mold, clamping unit, injection unit, and hydraulic unit.
What is the process of moulding?
The manufacturing process of molding (American English) or moulding (British English; note spelling variants) involves the shape of a liquid or malleable raw material using a rigid frame called a mold or matrix. It’s possible that this was constructed from a pattern or model of the finished product.
What are 3 types of plastic processing?
The process of plastic extrusion involves heating plastic and then forcing it through a heated barrel using a screw. Molding entails forcing plastic into a die to form the desired shape. As a last step, the plastic that has been extruded is cooled.
What are the parts of mold?
Mold components work to provide a superior end result. Mold bases, pins, ejectors, lifters, bushings, guides, and alignment devices are important. Frame plates, frame components, and cavity tooling are mold components.
What is an injection unit?
The injection unit’s job is to heat the plastic until it melts into a smooth, even mass that can be injected into the mold under the control of pressure and flow rate. Fluoropolymers are hard to work with because their thermal conductivity is low, their specific heat is high, and their melt viscosity is high.
What means molding?
Molding is a decorative piece of material used to adorn the top or bottom of a wall, a door, a window, or a piece of furniture. It can be created from wood, plastic, stone, or other materials.
What is injection moulding advantages and disadvantages?
Advantages of plastic injection moulding include excellent precision and repeatability, as well as speed, cheap cost per component, and a vast selection of polymers. The disadvantages include a greater starting cost and a longer lead time compared to other techniques.
What are the 4 stages of injection moulding?
The cycle is broken up into four distinct parts. Clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection are the phases that make up this process.
How does a molding machine work?
The plastic is melted until it becomes molten in the molding machine. The injection molding machine’s nozzle subsequently injects the molten plastic into the mold (injection pressure). The plastic liquid has now been poured into the mold’s cavity. This will then cool and solidify into a product.
What products are made by injection moulding?
This technique has been used to create a wide variety of solid components, including electronic housings, bottle caps, containers, computers, television components, outdoor furniture, agricultural items, toys, and components for equipment, to name just a few examples.
What is the function of a molder?
The intermediate proofer sends pieces of pie crust to the molder, which shapes them into cylinders that are ready to go into the pans. There are different kinds of molders, but they all do four things: they sheet, curl, roll, and seal.
What is injection pressure?
The pressure at which the mold is filled is referred to as the injection pressure; in certain cases, this pressure is also referred to as the first-stage pressure. The holding pressure is the pressure that is kept on the melt after the mold is filled and continues until the gate freezes or the pressure is withdrawn by the cycle timer control. This pressure is maintained on the melt for the duration of the holding period.
What is injection capacity?
The term “Injection Capacity” refers to the maximum amount of Natural Gas that can be injected per hour, measured in cubic meters, and held by the Provider on demand for the Customer in accordance with the terms of the Storage Service
Which motor is used in injection Moulding machine?
Injection Molding Machines employ low- and high-voltage liquid-cooled three-phase asynchronous motors.
What is servo in injection molding machine?
Servo motors are utilized in place of standard AC motors in a machine that is used for servo injection molding. The machine’s many drives, such as pump motors and injection drives, are all capable of being operated by servo motors. When compared to standard AC motors, servo motors provide a number of benefits.
What tools are used in injection moulding?
Plate will be moved halfway back.
BoltssRisers
Feet for the ejector plate.
Locating plate for the ejector and the retainer for the ejector plate
Bolster sleeves
The shifting of the partial support plate
Deflection bushes
plate for keeping the core
Core of Mould
Cavity for Mould
THE MOULDED PART
Guide pins
Plate for the retention of cavities
Sprue bush Half-back plate with a fixed sprue
Ring for locating the bolts
What is the function of electric motor molding machine?
Because electric motors are turned on only when they are required to perform their function, machines that employ this type of propulsion may achieve very high levels of energy efficiency. In addition, the cutting-edge energy recovery system is capable of capturing kinetic energy, storing it, and then employing this energy to power the device.
What is hybrid injection molding machine?
Some of a hybrid injection molding machine’s motions are powered by electric motors, while others are powered by hydraulics (in some rare cases, air). This enables for some of the advantages of electric drive systems to be realized without the corresponding increase in expense.
How long do injection molds last?
You can get hundreds of thousands of uses out of a plastic injection mold. Environmental conditions, upkeep, design, and SPI rating are just a few of the variables that affect how long an injection moulding mold will endure.
Why hydraulics is used in injection moulding?
Hydraulic injection molding is used to actuate core pulls, ejectors, valve gates, and thick-walled products with lengthy hold periods. Its advantages over all-electric include: Large clamping force. More injections.
What is difference between hydraulic and electric injection molding machine?
Electric Injection molding machines are fitted with digitally controlled servomotors that precisely regulate every operation, including injecting, extruding, clamping, and ejecting, to an incredibly high degree of accuracy, in contrast to hydraulic machines, which rely on hoses, valves, and pumps.
What is the Labour hour rate?
okay, so let me list two things If you’re wondering what you should pay the workers you’ve brought on board at your factory, I’d estimate a monthly salary of PKR 50,000 and an hourly wage of 185 (both of which are flexible depending on market conditions).
In addition, when customers acquire a mold along with plastics’ raw ingredients and then outsource the operation to someone with an injection molding machine, they typically pay a fee of 60 to 70 rupees per kg of plastic molded.
What is the formula for labor rate?
Start by tallying up the kilograms per hour of material output, then add in the cost per kilowatt hour of power used, and finally figure in the total cost of running your firm, including wages, taxes, and other overhead.
How do you calculate MHR for injection molding?
For the machine hour rate, we use the formula: machine hour rate = fixed/standing charges per hour + running expenses per hour.
What is cycle time in injection moulding?
The overall time necessary to complete all phases of the injection molding cycle is referred to as cycle time. The following phases comprise the cycle time: Time to fill. The amount of time it takes to fill the mold with polymer.
What is core and cavity?
The ultimate form of a plastic product is determined by the shape of the core and cavity, two shaped parts located in opposite halves of the mold tool. After being poured into the core and cavity at high pressure, the molten material cools and hardens into its final form. Having the right core and cavity design is crucial to making a quality end product.
What is cavity pressure?
What exactly is the definition of “cavity pressure”? A important measure of the quality of the molded object is the cavity pressure, or the pressure within the injection mold after it has been filled with molten plastic.
What is a 2-cavity mold?
A multi-cavity mold is one in which many components may be manufactured in a single molding cycle. A 4-cavity mold is a temporary solution for mass manufacture of similar components. The term “2+2 cavity mold” is commonly used to refer to a mold that can manufacture two sets of mirrored components, such as left and right-side pieces.
What is injection time?
The duration required for the mold to be totally filled is known as the injection time. The software may be adjusted so that an injection time for the machine is either automatically determined or determined based on a user-specified value while a Fill Pack analysis sequence is being set up. The inject time is determined mechanically by default.
What is the minimum thickness of plastic components?
We suggest a minimum wall thickness of 0.025 to 0.030 (0.635 to 0.762mm) for small parts and 0.040 to 0.050 (1.02 to 1.27mm) for bigger components to ensure smooth, high-volume manufacturing.
What is the difference between a standard injection molding machine and a servo injection molding machine?
Servo injection molding means servo valve control, servo-drive, or servo-motor. Servo-drive IMMs are hydraulic machines with variable-speed servo motors driving high-quality, low-noise pumps. Larger machines require additional servo motor+pump units. All-electric machines employ servo motors, but not hydraulic pumps. Servo-motor IMMs are as efficient as all-electric but offer more speed and power.
Standard IMMs use AC motors (which run at a set speed) and pumps, invariably variable volume pumps on later devices. Though cheaper than servo-motor or all-electric, they’re more expensive to run. Variable speed motors can be added to standard IMMs to improve energy efficiency.
Servo injection molding machines have servos.
Standard injection molding isn’t
Servo system includes servo motor,controller,oil pump.
In industry, saving power means saving money.
Servo machines are more costly than standard.
Servo motors replace AC motors in Servo Injection Molding machines. Servo motors can be utilized in pump and injection drives.
Servo motors are superior to AC motors. They’re accurate, light, quiet, and use less power. However, they’re expensive.
Servo injection molding machine features:
Strong grip
Less power use
Cycle time faster
Silent machine and clean molding
Position, pressure, and pace are spot-on.
What is maximum daylight in injection molding?
In order to calculate the total amount of daylight available, we need to multiply the mold’s maximum height by the open stroke. The minimum amount of available light in a room is defined by the sum of the mould open stroke plus the mould height. Maximum daylight is calculated as minimum mould height plus mould open stroke when using a hydraulic clamp machine.
Which is the best injection Moulding machine?
The short answer is “Hi-Tech Plastics Engineering,” although it might be confusing. The size and intricacy of the product you are making will determine the type of molding machine that will serve you best.
How do you calculate shot size in injection molding?
So, convert 164 g PP to PS for your shot size. 164 g/28.3 g/oz 1.04/0.90 or 6.72 oz comparable to PS.
What is L D ratio in injection Moulding machine?
The length to diameter (L/D) ratio is another essential ratio that should be taken into consideration. This is the ratio that is calculated by dividing the flighted length of the screw by the screw’s nominal outer diameter. Although there are currently various manufacturers of injection molding machines that provide a selection of injection units, the vast majority of injection screws employ a ratio of 20:1 L/D.
How do I choose a molding machine?
In order to choose the appropriate unit for your plastic injection molding machine, you need to have knowledge of the following parts: the type of plastic being used, the cycle time, the cooling time, the shot weight (including the weight of the part, the cold runner, and the number of cavities), and the number of cavities. Peak injection pressure required Rates of plasticizing and injection are examples of rates. Maintain the time and the pressure.
How do you control flow marks in injection Moulding?
Managing Flow Separations
Raise the input parameters, such as injection rate, pressure, and material temperature. Flow lines form more often in molten plastic that moves slowly because of the increased likelihood of rapid cooling.
Where the wall thickness grows, round the edges of the mold: Thus, the flow rate is maintained uniformly over the thicker parts, and flow lines are avoided.
How do you reduce part weight in injection molding?
By regulating the melt’s temperature and pressure just before the gate freezes, the lT technique allows for precise control of the part’s mass. This is when the cavity melt pressure begins to drop after reaching its maximum.
What is the unit of injection speed?
The injection rate (the amount of molten plastic injected in one second, cm3/s) or the injection speed (the pace at which the plunger moves forward, mm/s) are two measures of the effectiveness of an injecting unit.
What is the unit of injection pressure?
The injection pressure for injection molding may range anywhere from 15,000 to 20,000 pounds per square inch (psi) (103–138 MPa). The typical pressure of an injection molding machine is 20,000 pounds per square inch.
What is difference between vertical and horizontal injection molding machine?
Horizontal inserts were put on a mold base, whereas vertical inserts were mounted directly on the machine (without a mold base). C-clamps held the latter’s insert closed during injection.